A healthy lifestyle is rarely associated with potassium intake . It is the main essence without which the human body cannot function properly . Find out more about the surprising effects of potassium to prevent health problems caused by potassium deficiency.
Potassium and its functions in the body
Potassium is an essential mineral which is the basic element for the proper functioning of all cells and tissues in the human body. It affects the heart muscle, but also the skeletal and smooth muscles , which are involved in neuromuscular transmission.
Potassium occurs as a cation in the human body . The organism contains approximately 98% potassium directly in the cell and the remaining 2% is present outside the cell. Overall, it is mainly in muscles, red blood cells, liver, skin, bones, nerves, brain or body fluids . {3 ]

The absorption of potassium takes place in the intestine and is in the urine and partially also excreted on the face. The amount of potassium we excreted depends on the amount of this element received. People who do not get potassium from food or supplements have dramatically less potassium in their urine. Particular caution is required with athletes , as they warn the body and then sweat during the instructor to increase the loss of potassium. Athletes are therefore advised to increase their potassium income.
The human body needs at least 1000 mg of potassium per day to ensure all important processes. We can complement it with fruits, vegetables, legumes or some fish . Given current eating habits, people often suffer from potassium deficiency, which can also be life threatening.
The most important effects of potassium
Potassium and sodium form a balance system in the human body , which controls the water management in the tissue and contributes to the proper functioning of the kidneys. Aside from this benefit, potassium has a variety of other health benefits.
1. It lowers blood pressure and the risk of cardiovascular disease
Sodium is mainly responsible for the correct potassium balance. Low potassium and high sodium can lead to high blood pressure. For this reason, it is important to combine increased potassium consumption with lower sodium consumption in order to prevent cardiovascular diseases. Hypertension affects up to 95% of patients . Studies have shown that potassium supplement can significantly lower blood pressure in people struggling with high blood pressure who also consume a lot of sodium.
Up to 38% of patients with high blood pressure who ate a diet high in potassium had their blood pressure under control without treatment.
The reduction in the risk of cardiovascular disease was also investigated in a study on a group of people who received 4 g of potassium per day. The result was an up to 49% lower risk of dying from ischemic heart disease than in the group that received only 1 g of potassium per day.
2. It maintains healthy bones and muscles
Foods that are rich in potassium keep the body in an alkaline environment in contrast to acidosis. Metabolic acidosis is caused by a diet high in acidic foods such as meat, dairy products, and processed grains. Acidosis, or disorder of internal homeostasis, is a common consequence of a typically acidic Western diet.
Acidosis can lead to nitrogen excretion and thus to a loss of mineral density in bones and muscles . Eating foods high in potassium helps protect muscle mass in the elderly, as well as in those with diabetic ketosis, which can lead to muscle wasting. Potassium may be an appropriate prevention of this disease. [18chievement ]
Some studies also show that a higher potassium income leads to an increase in bone density can lead . Potassium income was found to be related to the maintenance of calcium levels in otherwise healthy adults. On the other hand, a lower potassium income is associated with a higher calcium loss in the urine , while an increase in the potassium income decreases the calcium loss in the urine .
An example of this is the study in which postmenopausal women suffering from osteoporosis have been taking potassium for a year. The research resulted in a decrease in some biomarkers of bone turnover. This shows the protective effect of potassium on mineral bone density . Regarding the importance of potassium for muscles, one study found that participants who took 5,266 mg of potassium a day had an average of 1.6 kg more lean tissue mass than those who received 50% less potassium.

3. It protects the kidneys and reduces the risk of kidney bones
The researchers studied the effects of potassium in hypertensive rats. It has been shown that higher doses of potassium are effective in protecting the kidneys after a stroke compared to the group with the lower potassium income. This effect did not affect blood pressure. Potassium intake can prevent kidney inflammation. Especially in combination with magnesium it helps against kidney damage caused by cyclosporine, substances whose side effect is kidney failure.
Kidney stones occur when the urine contains a high concentration of calcium. As mentioned above, the potassium income will decrease the amount of calcium in the urine and may prevent the formation of kidney stones . Studies have also confirmed this. In women who received more potassium, the likelihood of kidney stones could be reduced by up to 35%. Taking potassium in the form of potassium citrate even reduces the occurrence of repeated kidney stones.

4. It helps as a prevention against stroke and vascular attacks
People who eat 3 to 5 servings of fruits and vegetables with high potassium content per day can increase the risk of strokes and Reduce vascular seizures by up to 26% compared to people who ingest less than 3 servings. The reason is the effect of potassium from fruits and vegetables on blood pressure when combined with fiber. The main risk factor for stroke is high blood pressure. One study followed Americans over 12 years. An increase of 390 mg potassium per day was associated with a 40% lower stroke mortality in adults aged 50-79 years.
Potassium’s potential protective effects have been demonstrated by studying its effects on stroke prevention . Studies showed a 21% reduction in stroke with an increase in potassium income of 1.64 g per day. [23 Autovermietung
5. It helps prevent diabetes
Diabetes, which will be lifelong with diabetes, has much bigger problems with the liver than with the pancreas. And it is potassium that interferes with the proper functioning of the liver . When a person has low potassium levels, they cannot store sugar where it needs to be – in the muscles and in the liver. A body without potassium converts sugar into fat. After this process, the sugar level drops again and the body needs additional sugar. Although the body wants to consume more sugar, it actually lacks potassium. In fact, low levels of this mineral decrease glucose tolerance, which is associated with decreased insulin release, leading to significant changes in glucose metabolism. [21] [22]
Studies also show that high potassium income results in a 39% reduction in the risk of metabolic syndrome in men and Connected to women.
Why is potassium so important for athletes?
During exercise, a significant amount of potassium sweating eliminated. The more intensely you exercise , the more potassium you sweat. So if you exercise for more than an hour a day, or do endurance sports like cycling or running, pay attention . Potassium can have the following advantages for you:
1. It helps prevent flatulence and water retention
Too much sodium in food leads to water retention in the body and the associated flatulence . It is potassium that is key to preventing this from happening. Immediately after consumption, sodium and water are absorbed into the cells together. The water is then deposited between muscles and skin in the body , which leads to gas. Remembers how you felt after your last fast food or salty meal. Potassium is the ideal solution to this problem. [27 ]
The intake of potassium influences the electrolyte balance . This means that using an electrolyte pump, potassium pushes sodium and water out of the cells. This excretes sodium and water in the urine and rebalances the internal environment. This advantage is particularly praised by athletes as it solves the problem with bloated stomach and water retention .

2. It affects the overall function of the muscles
Different concentrations of potassium and sodium inside and outside the cells create electrical charges that help the nerves To send signals to the brain. Thanks to them, we can move the muscles. In this way, potassium affects contraction and relaxation of the muscles, which allows our body to exercise. In addition, it helps with muscle regeneration and prevents muscle spasms.
3. It is used in the breakdown of glycogen
Potassium is part of the process of breaking down glycogen in muscle cells, that the cells with energy during endurance training supplies . When glycogen breaks down, the cells in the muscles use up the potassium that enters the bloodstream or leaves the body through urination or sweating. [31] Potassium is part of the process of breaking down glycogen in muscle cells, which supplies the cells with energy during endurance training. When glycogen breaks down, the cells in the muscles use up the potassium that enters the bloodstream or leaves the body through urination or sweating. [28 ]
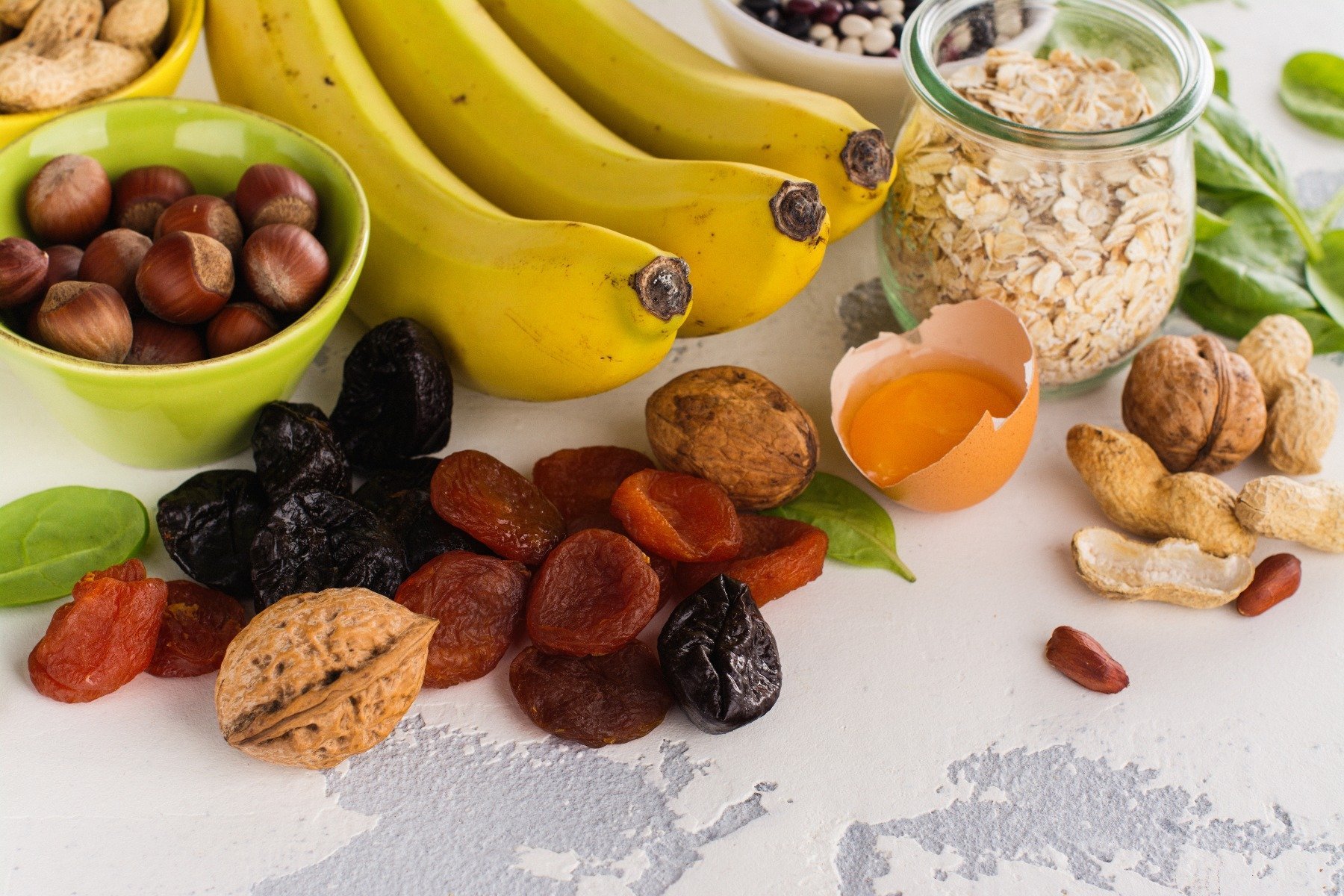

The best food sources for potassium
Mainly, unprocessed foods are a rich natural source of potassium . In fruit there are mainly apricots, avocados, bananas, melons, figs, grapefruits, kiwis, mangoes and citrus fruits . Vegetables are especially green and leafy vegetables such as spinach, cabbage, lettuce or broccoli. Other sources are artichokes, bamboo shoots, legumes such as beans, lentils, peas, but also bran and chocolate. [15 ]
The presence of potassium in an amount of 100 g per food can be taken from the table .
| Food | Amounts of potassium per 100 g |
|---|---|
| Bananas | 350 mg |
| Wheat Bran | 1160 mg |
| Soy | 1660 mg |
| Boiled eggs | 180 mg |
| Unprocessed apricots | 1880 mg |
| Unprocessed figs | 1010 mg |
| Dried peaches | 1100 mg |
| Dried raisins | 860 mg |
| Chicken | 300 mg |
| Pistachios | 970 mg |
| Milk chocolate | 420 mg |
| Bamboo shoots | 535 mg |
| Parsley | 1080 mg |
| Curry Pepper | 1840 mg |
Recommended potassium income
The daily potassium income should be at least 2 g per day for adults and healthy people. However, the optimal potassium income is up to 4.7 g per day , while breastfeeding is even 5.1 g. People with diabetes, high blood pressure or liver dysfunction should consider a higher potassium income in consultation with a doctor. The required potassium dose depending on age, gender and stage of life can be found in the table .
- Up to 6 months400 mg400 mg7 – 12 months700 mg700 mg
1 – 3 years3000 mg3000 mg
4 – 8 years3800 mg3800 mg
9 – 13 years4500 mg4500 mg
14 – 18 years4700 mg4700 mg4700 mg5100 mg
| Age | Men | Women | Pregnancy | Breastfeeding |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 19 – 50 years | 4700 mg | 4700 mg | 4700 mg | 5100 mg |
| 51+ years | 4700 mg | 4700 mg |
Research in the United States has shown that less than 2% of Americans get enough potassium, while women consume even less of this element than men. [1] A study on Slovaks of different sexes and ages confirmed low potassium levels in the body of older people. The results also varied due to the physical activity of the participants.
If you cannot take the recommended potassium dose as a diet, you should take the appropriate dietary supplement. Risk groups are people with little fruit and vegetable consumption, seniors, alcoholics, athletes and people with a lot of physical strain.
Even if you are on a weight loss diet with fewer than 1000 calories a day, there is still a risk of potassium deficiency. You should therefore consider adding supplements.

Potassium deficiency
Long-term low potassium levels in the body cause hypokalemia, which is the result of excessive excretion of potassium from the body and inadequate dietary supplements. This particularly applies to:
- Athletes who exercise more than an hour a day
- People on a low-calorie diet
- all with digestive problems and diarrhea
- people with eating disorders
- diabetics
- people with kidney disease
- alcoholics
Hypokalemia is the body’s response to frequent urination, sweating, diarrhea, or vomiting that leaches a lot of minerals from the body. Potassium deficiency shows symptoms like:
- swelling
- hypertension
- arrhythmia
- arthritis
- Nervousness
- increased tiredness
- muscle weakness
- coprostasia
hypokalemia can be detected by blood tests. When potassium levels drop to 2.2-2.5 mils, it’s a life-threatening condition that can cause body paralysis, muscle failure, breathing problems and even fatal arrhythmias. [18] [25] The positive effects of potassium and the negative effects of potassium deficiency are the reason why we need to monitor and replenish potassium levels regularly.
Excessive Potassium Income
Too high potassium levels in the body is known as hyperkalaemia and can lead to severe and significant metabolic disorders . This is a situation where potassium levels rise rapidly to 5.3 to 8 mils. per liter with an optimal limit of 3.6 to 5.2 mils per liter. A slight increase shows up as:
- muscle pain
- tiredness
- nausea
- tingling in the limbs
Low pressure, cardiac arrhythmias , in the worst case cardiac arrest, are considered serious symptoms of hyperkalemia. However, you don’t have to worry. By consumption of fruits, vegetables and an optimal amount of nutritional supplements, you cannot consume too much potassium. Hyperkalemia occurs only in patients with impaired renal function or diabetics on. Extreme potassium intake in healthy individuals can cause vomiting or the excretion of excess potassium in the urine.
